Table of Contents
Introduction: (Epiphyseal Plate)
The human body is a complicated and intriguing entity that constantly develops and adapts over the course of a person’s lifetime. Growth is one of the most amazing processes we go through, especially in childhood and adolescence. The epiphyseal plate, a tiny but vital structure found in our bodies’ long bones, is at the center of this era of transformation. To better understand the miracles of human growth, we will delve into the complexities of the epiphyseal plate in this blog article, looking at its anatomy, function, and the factors that affect its activity.
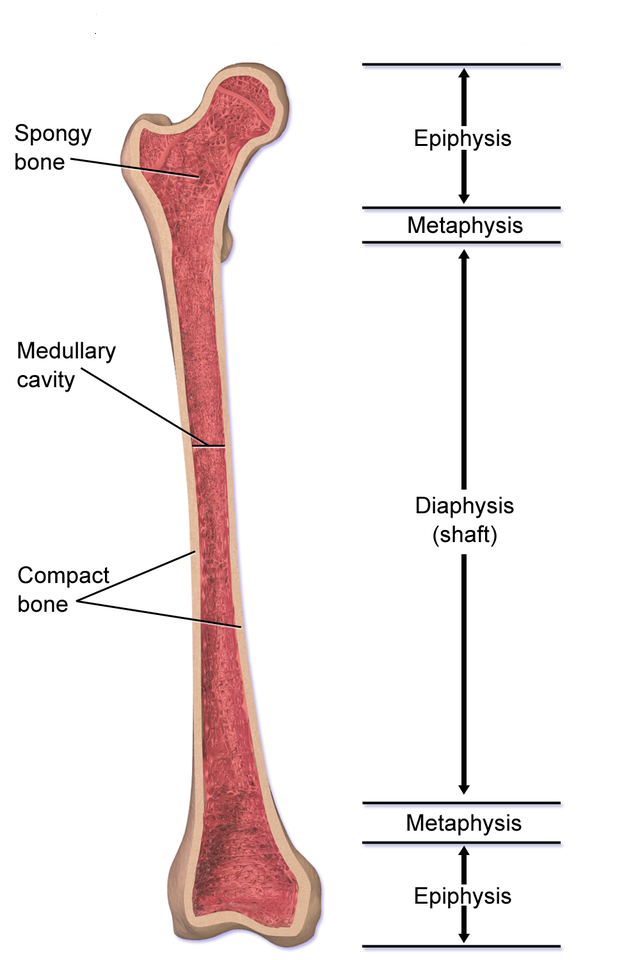
What is the Epiphyseal Plate
Long bones, such as those in the arms and legs, have a thin covering of cartilage called the epiphyseal, which is also known as the growth plate. This cartilage serves as a link between the bone’s diaphysis (the shaft of the bone) and epiphysis (the rounded end of the bone) during the growing years. The epiphyseal plate is in charge of longitudinal bone growth, which causes bones to elongate and add to an individual’s height.
The Role of Growth Hormones:
A complex interaction of hormones, with growth hormone taking centre stage, orchestrates bone growth. Growth hormone, which is made by the pituitary gland, stimulates the epiphyseal plate to promote cell division and the generation of fresh cartilage cells. Following their maturation into bone cells, or ossification, these chondrocytes stretch the bone.
Stages of Bone Growth:
Proliferation and ossification are the two main steps of the process of bone growth. The epiphyseal plate’s chondrocytes divide quickly during the proliferation phase, causing the cartilage to enlarge. Older cells migrate towards the diaphysis when new cartilage is formed. The elder chondrocytes mineralize and transform into bone tissue during the ossification phase, eventually joining the diaphysis and epiphysis to signal the end of growth at that particular bone end.
Factors Affecting Growth Plate Activity:
The epiphyseal plate’s activity can be influenced by a number of things. The potential height and growth pattern of a person are significantly influenced by genetics. The vital elements required for bone formation must be provided through adequate nutrition, especially during childhood and adolescence. Atypical development patterns might result from hormonal abnormalities like excess or insufficient growth hormone. Injuries to the growth plate can also impair its functionality, reducing bone formation and raising the possibility of growth problems.
Peak Height Velocity and Puberty:
Peak height velocity (PHV), a phase of rapid growth that occurs as children approach puberty, takes place. The epiphyseal plate’s activity is at its peak during this time, which causes noticeable height gains. PHV typically strikes girls between the ages of 11 and 12, while it typically strikes boys between the ages of 13 and 14. When the epiphyseal plate merges and closes, height growth becomes noticeably slower.
Epiphyseal Plate Injuries:
The epiphyseal plate is unfortunately prone to damage, especially in young sports and active kids. The normal growth process can be hampered by damage to the growth plate, which can lead to malformations or unequal limb lengths. The likelihood of such injuries can be decreased by taking preventative steps, such as wearing the right protective gear and using the right skills when engaging in physical activity.
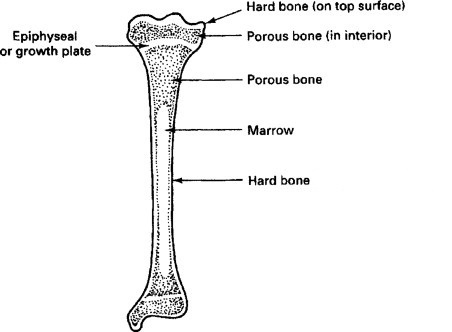
Clinical Importance:
Understanding the epiphyseal plate is crucial for identifying and treating disorders that are connected to growth in the medical field. For instance, through medical examinations, growth hormone shortages can be detected early and the proper treatments can be started to maintain healthy growth. X-rays are frequently used by doctors to track the growth of the epiphyseal and spot any potential problems with bone development.
Final Thoughts
The epiphyseal plate, which supports the wonderful process of growth in our bodies, is a true miracle of nature. As we age, we may reflect with wonder on the pivotal years when this little structure made a significant impact on our height and overall physical development. By highlighting the value of a healthy diet, consistent exercise, and good healthcare, we can make sure that the epiphyseal plate performs to the fullest extent, helping us to achieve the heights of our aspirations.
FAQ’s
Q1. What is the epiphyseal plate, and where is it located in the body?
A. Long bones, such as those in the arms and legs, have a thin covering of cartilage called the epiphyseal plate, which is also referred to as the growth plate. It serves as a link between the bone’s diaphysis (the shaft of the bone) and epiphysis (the rounded end of the bone).
Q2. What is the role of the epiphyseal plate in human growth?
A. Longitudinal bone growth depends on the epiphyseal plate. It permits the elongation of bones during childhood and adolescence, which adds to an individual’s overall height.
Q3. How does the epiphyseal plate function during the growth process?
A. During the two main phases of bone growth, the growth plate passes through. During the proliferation stage, chondrocytes, which make up cartilage, divide quickly, causing cartilage to grow. Older cells migrate towards the diaphysis when new cartilage is formed. The epiphysis and diaphysis unite during the ossification stage when the older chondrocytes mineralize and change into bone tissue.
Q4. What role do growth hormones play in the activity of the epiphyseal plate?
A. The epiphyseal plate is stimulated by growth hormones, especially those produced by the pituitary gland, to enhance cell division and generate new cartilage cells. Ossification is the process that causes bone to lengthen and expand.
Q5. What factors can influence the activity of the epiphyseal plate?
A. The activity of the growth plate can be significantly influenced by genetics, diet, and hormones. The nutrients required for good bone growth must be provided through proper nutrition during childhood and adolescence. Growth can be impacted by hormonal abnormalities, such as excess or insufficient growth hormone. Injuries to the growth plate can also impair its functionality and perhaps cause problems with growth
Q6. Peak height velocity (PHV), when does it happen, and what does it mean?
A. The fastest growth occurs during the peak height velocity (PHV) stage of puberty. PHV typically strikes girls between the ages of 11 and 12, while it typically strikes boys between the ages of 13 and 14. PHV is a significant benchmark that shows the epiphyseal plate is actively contributing to height growth.
Q.7 Can the epiphyseal plate be protected from injuries?
A. While it can be difficult to totally eliminate accidents, there are several precautions that can be taken to lessen the chance of growth plate damage. The incidence of such injuries can be reduced by using good technique and safety equipment when participating in physical activity and sports.
Q8. What role does understanding the epiphyseal plate play in therapeutic practice?
A. Medical experts use their understanding of the epiphyseal to identify and treat disorders that are connected to growth. Early detection of growth hormone deficiency and other problems with growth enables prompt management and support for healthy growth.
Q9. What methods are used in medical contexts to monitor and assess the epiphyseal plate?
A. X-rays are frequently used by doctors to evaluate the growth of the epiphyseal plate and identify any potential issues with bone growth. These pictures offer insightful information on how children and teenagers develop.
Q10. How can we guarantee that children and adolescents grow as best they can?
A. Supporting healthy growth during childhood and adolescence requires maintaining a balanced diet, participating in regular physical activity, and seeing a doctor on a regular basis. These elements, along with knowledge of the role of the epiphyseal plate, can help someone realise their maximum growth potential.
