Table of Contents
Introduction: (Diabetes Symptoms)
It is essential to be aware of the symptoms associated with diabetes to ensure early detection and proper management. In this article, we will explore the various symptoms of diabetes and discuss when to seek medical attention.
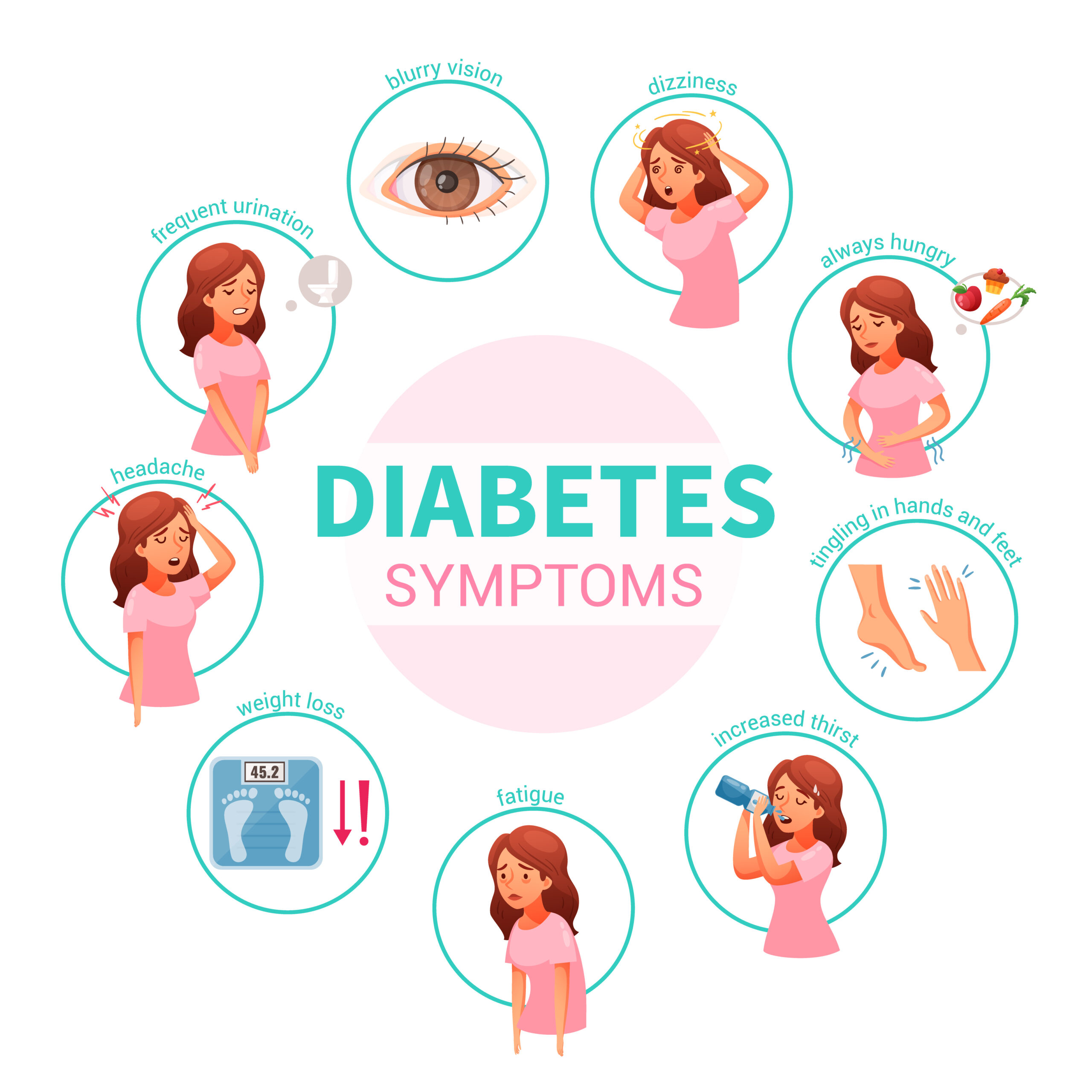
Diabetes Symptoms
What is Diabetes ?
Diabetes represents a condition of metabolic imbalance where elevated levels of glucose exist within the bloodstream. This ailment arises from insufficient production of insulin by the body, which acts as the regulator for blood sugar, or from the body’s inability to efficiently utilize the insulin it generates.
Types of Diabetes:
There are three main types of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes, commonly referred to as juvenile diabetes, typically arises during childhood or early adulthood. It emerges when the immune system erroneously targets and destroys the cells in the pancreas responsible for producing insulin. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes necessitate continuous insulin therapy throughout their lives.
Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes stands as the prevailing variant among diabetes cases, encompassing a significant majority of diagnosed instances.. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor diet, and lack of physical activity contribute to the development of Type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes:
Gestational diabetes emerges specifically during pregnancy and impacts certain women who have not previously experienced diabetes. The hormonal fluctuations that occur during pregnancy can induce insulin resistance, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Although gestational diabetes typically resolves following childbirth, it heightens the likelihood of developing Type 2 diabetes in the future.

Common Diabetes Symptoms :
Recognizing the early symptoms of diabetes is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management.
Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination:
Excessive thirst (polydipsia) and frequent urination (polyuria) are classic signs of diabetes. High blood sugar levels can cause the kidneys to work harder to filter and absorb the excess sugar, leading to increased urination. This, in turn, causes dehydration, resulting in increased thirst.
Unexplained Weight Loss:
Sudden weight loss without any significant changes in diet or physical activity may indicate diabetes. The body is unable to utilize glucose properly in diabetes, so it starts breaking down fat and muscle for energy, leading to weight loss.
Fatigue and Weakness:
Feeling tired and fatigued, even after adequate rest, is a common symptom of diabetes. High blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to convert glucose into energy, resulting in fatigue and weakness.
Blurred Vision: (Diabetes Symptoms)
Blurry vision or difficulty focusing can occur when high blood sugar levels affect the fluid levels in the lenses of the eyes.
Slow Healing of Wounds:
Diabetes can affect the body’s ability. High blood sugar levels can impair blood circulation and damage blood vessels, leading to delayed wound healing.
Tingling Sensation in Hands and Feet:
Nerve damage (neuropathy) is a common complication of diabetes. Tingling, numbness, or a pins-and-needles sensation in the hands and feet may occur due to nerve damage caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels.
Recurring Infections:
Diabetes weakens the immune system, Frequent infections, particularly urinary tract infections, skin infections, and yeast infections, may be a sign of diabetes.
Changes in Skin and Itching:
Diabetes can cause skin changes such as dryness, itchiness, and darkening of the skin. These changes often occur in areas where skin folds or creases, such as the armpits, neck, and groin.

Diabetes Symptoms
Less Common Symptoms of Diabetes:
While the symptoms mentioned above are more prevalent, diabetes can also manifest in less common ways. These include:
Dry Mouth and Increased Hunger:
A persistently dry mouth (xerostomia) can be a symptom of undiagnosed diabetes. Additionally, increased hunger (polyphagia) can occur when the body does not utilize glucose properly, leading to persistent hunger pangs.
Erectile Dysfunction:
Diabetes can affect blood flow and nerve function, leading to erectile dysfunction (impotence) in men. It is important to address this issue and seek appropriate medical advice.
Dark Patches on the Skin:
Dark patches of skin, known as acanthosis nigricans, can develop in individuals with diabetes. These patches are usually found in body creases and folds and may be an early warning sign of insulin resistance.
Mood Swings and Irritability:
Unstable blood sugar levels can affect mood and lead to irritability, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating. Managing blood sugar levels can help stabilize moods and improve overall well-being.
Foot Problems and Numbness:
Nerve damage due to diabetes can cause peripheral neuropathy, leading to numbness, tingling, or a burning sensation in the feet. Proper foot care and regular check-ups are essential to prevent complications.
When to Consult a Doctor:
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above or have concerns about your health, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and proper management of diabetes can prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes.
Conclusion:
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes is vital for timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By understanding the warning signs and seeking medical advice when necessary, individuals can take control of their health and effectively manage diabetes.
FAQ (Diabetes Symptoms)
Q. Can diabetes be cured?
A. Diabetes is a chronic condition that cannot be cured. However, it can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular medical care.
Q. Are all diabetes symptoms the same for everyone?
A. Symptoms can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience all the common symptoms, while others may have only a few or none at all. It is important to be aware of your body and seek medical advice if you have any concerns.
Q. Can diabetes develop suddenly?
A. In some cases, diabetes can develop suddenly, especially in Type 1 diabetes. However, Type 2 diabetes often develops gradually over time, and symptoms may go unnoticed for an extended period.